Chapter 3 Essential Questions: when doing extended research and writing assignments for this weeks topic consider these essential questions:
- What is direct instruction and how to teach a lesson using direct instruction?
- What is the best way to teach for transfer of learning?
- In what ways does knowledge of effective lessons inform intentional teaching?
- Upon viewing related videos, topical dialogue, reading of chapter content related to lesson planning and direct instruction, graduate candidates will seek out related scholarly work which will be evaluated at a B or better using the annotated bibliography rubric.
Topic 1: What is direct instruction and how to teach a lesson using direct instruction?
"The term direct instruction is used to describe lessons in which you transmit information directly so students, structuring class time to reach a clearly defined set of objectives as efficiently as possible" (Slavin, 2018, p. 160).
Intro to DI: What is Direct Instruction
Topic 1 Student Activity 1: (Think -Pair - N - Share) considering the following questions after viewing the above video:
- From what you have viewed, what can be said about Classical Conditioning and Classroom Management?
- In what ways would you relate Direct Instruction to a Information-Process Model? Explain and provide some examples.
- Consider cognitive theory (Piaget schema, stage theory) & How did Vygotsky view cognitive development)
- What is direct instruction and how to teach a lesson using direct instruction? (Consider is direct instruction more suitable for skill and strategy instruction?)
Topic 2: What is the best way to teach for transfer of learning?
Slavin (2018) provides the following parts of a direct instruction lesson plan:
- State learning objectives and orient students to the lesson.
- Review prerequisites
- Present new material
- Conduct learning probes
- Provide independent practice
- Assess performance and provide feedback
- Provide distributed practice and review (p. 161)
Example: Identify the ABCD parts of the objectives below.
- Given a standard sentence, the English 101 student should be able to identify the noun and verb without error.
- When given several different scrap materials, 4th grade students will create a flower model, identify the flower parts, inclusive of the the necessary reproductive parts and write the means in which their plant reproduces at the 80% or better.
Topic 2 Student Activity 2: As noted in the Sample Lesson Plans found on your text pages 162 and 163 defend that these are goals and not objectives. Following the ABCD Method, change to measurable objectives.
Extended Study: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED571537.pdf
Topic 3: In what ways does knowledge of effective lessons inform intentional teaching?
Direct Instruction and Blooms Taxonomy:
Bloom's Taxonomy: Asking students to think at higher levels, beyond simple recall, is an excellent way to stimulate students' thought processes. Lessons as well as the different types of questions require us to use different kinds or levels of thinking.
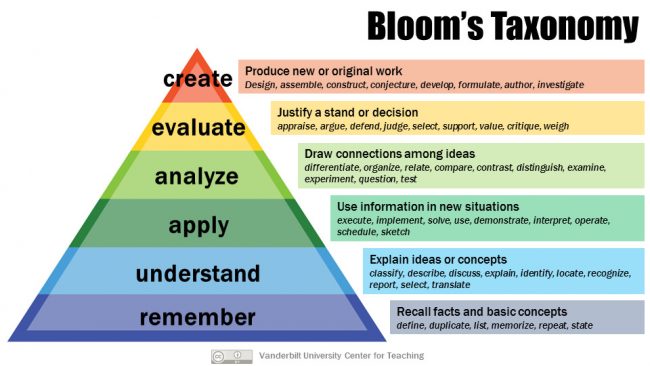
Topic 3 Student Activity 3: Conduct an internet search for a lesson, validate whether the goal and objective are written correctly. Evaluate at what level of Bloom's the lesson consists of. Prepare to discuss your findings.
- At what level (mostly) are the children's thinking based on Blooms Taxonomy?
- Is Direct Instruction appropriate for American Indian children, why or why not?
- Is Direct Instruction a means to pass standardized exams or to prepare our children to function in the adult world?
- In what ways is Direct Instruction inclusive of mastery learning or how is it not?
- In what ways, according to Bloom's Taxonomy, are we teaching for mastery?
- Within your school systems is the curriculum determining the instruction for mastery or is the teachers? Explain why or why not.
- What would be some means of improving instruction according to Direct Instruction and Bloom's Taxonomy?
Mastery Learning & Goals and Objective
Writing effective goals and objectives is vital to plan for instruction, to guide learning, and to see how the lessons goals and objectives have played out in the lesson. Goals and objectives, if written correctly, can indicate how well your teaching or lesson design has impacted student learning.
Closure: Engage in dialogue some thoughts about what research topics can be related to the topics covered so far.
- Read Chapter 7
- Annotated Bibliography 9 (address the essential questions)
Extensions: Just few things here which maybe of interest.
- National Institute for Direct Instruction: https://www.nifdi.org/what-is-di/intro-to-dihttps://www.nifdi.org/what-is-di/intro-to-di
- Evaluating Three Programs Using a School Effectiveness Model: Direct Instruction, Target Teach, and Class Size Reduction: http://eric.ed.gov/q=direct+instruction&ft=on&id=EJ874476
- Questioning Strategies: http://eric.ed.gov/?q=Questioning+Strategies&pr=on&ft=on
- What TIMSS Tells Us about Instructional Practice in K-12 Mathematics Education
- ANALYSIS OF LESSON PLANS: THE CASEOFENGLISH TEACHING IN KAFA ZONE
No comments:
Post a Comment